
The exchange of health-related data has become a pervasive aspect of modern society. It influences various sectors, shaping insights that can drive advancements in patient care and treatment options. Yet, while this exchange fosters innovation, it also opens the door to unique challenges. Every stakeholder has a role to play, whether it’s practitioners, researchers, or even businesses looking to capitalize on the wealth of insights available.
In recent years, the landscape of health information sharing has dramatically evolved. With increased digitization, personal details can be aggregated and dispersed at alarming speeds. The nuances of consent, privacy, and ethical considerations continually emerge as topics of rigorous debate. It is crucial to navigate these waters carefully, ensuring that the benefits of shared insights do not come at the cost of individual rights.
On one hand, there are undeniable advantages, such as enhanced research capabilities and improved public health strategies. On the other hand, the potential for misuse looms large. Concerns about how personal data is used–and potentially abused–are at the forefront of discussions surrounding this industry. Therefore, striking a balance between innovation and protection is essential in the evolving narrative of health information exchange.
This intricate web of interactions raises profound questions. Who really benefits from the analysis of these insights? How can stakeholders ensure that individuals are safeguarded against potential exploitation? As technology continues to advance, the importance of maintaining ethical standards cannot be overstated. Only through diligent oversight can we hope to harness the potential of health data while protecting the rights of those it represents.
Understanding Data Brokers in Healthcare
In the modern medical landscape, a variety of entities play crucial roles in the management and distribution of health-related details. These organizations, often operating behind the scenes, facilitate the flow of sensitive information. They gather, analyze, and share patient data, influencing many aspects of care delivery. This complex web of interactions can be both beneficial and contentious.
Primarily, these entities serve multiple stakeholders, including providers, researchers, and even insurers. Their significance stems from the ability to compile vast amounts of health-related insights. By doing so, they create a nuanced portrait of health trends that can guide clinical practices and policymaking. However, navigating the interests of different parties often leads to ethical dilemmas and privacy concerns that cannot be overlooked.
In essence, these organizations bridge gaps between healthcare providers and those seeking information for various purposes. They are involved in everything from clinical trials to market research. Their work often drives innovation in treatment protocols, contributing to improved patient outcomes. Still, this blending of roles raises questions about accountability and transparency.
Moreover, the sheer volume of personal information they handle can lead to questionable practices. Concerns about consent, security, and accuracy are paramount. The potential for misuse of sensitive data is an ever-present threat in this environment. As technology evolves, the methods used by these organizations also adapt, prompting ongoing debate about the moral implications of their operations.
Ultimately, while these entities can facilitate advancements in medicine, they must also navigate a landscape fraught with ethical challenges. The balance between innovation and safeguarding personal information is delicate. Stakeholders must engage in meaningful dialogue to ensure that advancements do not come at the expense of patient trust and confidentiality.
The Role of Data Brokers in Medicine
Within the realm of medical practices, a unique exchange occurs, allowing for the evolution of various entities involved. This practice encompasses elements such as patient insights and treatment outcomes, creating opportunities for innovation. It also bridges gaps between research, clinical applications, and administrative functions. These exchanges can lead to improved health services and personalized care, ultimately benefiting both providers and recipients.
Various players participate in this intricate network. They gather insights from numerous sources, promoting better efficiency and informed decisions.
- Enhanced resource allocation
- Informed clinical decisions
- Innovative research opportunities
- Health improvement initiatives
Understanding these exchanges is crucial. They yield significant knowledge that propels the industry forward. For instance, insights derived from aggregated patient data can lead to targeted therapies. This method enhances the efficacy of treatments and allows for a deeper analysis of outcomes. By synthesizing vast amounts of health-related information, practitioners can identify patterns and trends that may otherwise remain hidden.
Furthermore, this intricate exchange facilitates collaboration among various entities. Researchers gain access to invaluable insights, leading to groundbreaking studies. Pharmaceutical companies refine their product development based on real-world evidence. Hospitals and clinics can tailor their services, ultimately improving patient experiences. Such collaborative efforts elevate the standards of care provided to the community, which can have a profound impact on public health outcomes.
However, it is vital to balance these advantages with ethical considerations. Understanding the implications of shared insights ensures that patient autonomy is respected. Safeguarding sensitive information remains a priority, even amidst the benefits. As we navigate this evolving landscape, the potential for enhanced patient care continues to grow, driven by innovative practices and collaborative exchanges.
Potential Benefits of Medical Data Trading
In today’s interconnected world, the exchange of personal health records can yield significant advantages for various stakeholders. Sharing insights can lead to improved treatment methodologies, enhance research capabilities, and foster innovation in medical practices. However, the process is not without its complexities. Understanding the implications of this exchange is crucial for maximizing its potential.
One of the key benefits is the advancement of personalized medicine. By analyzing vast amounts of health-related materials, medical professionals can tailor treatments to individual patients. This customization increases the likelihood of successful outcomes and reduces unnecessary interventions. Moreover, it allows for proactive measures to be taken, ultimately enhancing the quality of care.
- Facilitates medical research and clinical trials.
- Enables more accurate predictions of patient outcomes.
- Encourages collaborative approaches across different institutions.
- Supports the identification of rare diseases and conditions.
Additionally, the sharing of information can lead to significant cost reductions in the medical field. When organizations access a broader spectrum of knowledge, they can streamline processes and eliminate redundancies. This efficiency not only saves money but also improves the allocation of resources. As a result, healthcare providers can focus more on patient care rather than operational challenges.
Furthermore, transparency in patient records bolsters trust between patients and healthcare providers. When individuals are aware that their health information is being used to enhance practices, they may feel more empowered to engage with their care plans. Trust leads to better patient-provider relationships, encouraging open communication and adherence to treatment protocols.
However, these advantages come with a caveat. Safeguarding privacy remains paramount amid the exchanges. While the benefits are compelling, ensuring that personal information is strictly protected is essential for maintaining public confidence in these systems. Thus, a balanced approach is necessary, weighing the gains against privacy concerns.
Ultimately, the potential growth of medical innovation hinges on the judicious sharing of health records among trusted entities. The landscape is continuously evolving, with technology paving the way for more efficient practices. This is an exciting time for the medical community as it explores the myriad advantages that stem from collaborative knowledge sharing.
Privacy Concerns Surrounding Health Information
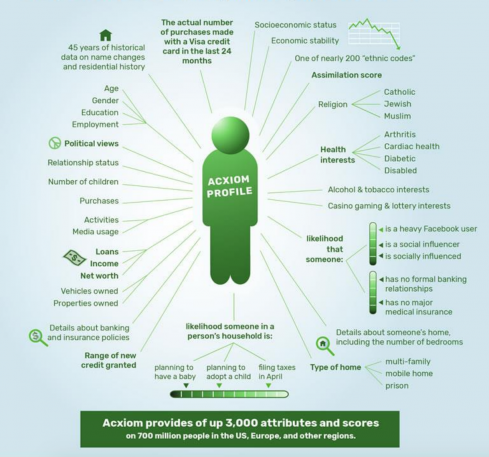
In an era where personal records are increasingly digitized, concerns about confidentiality have surged. With the rise of companies that specialize in collecting and sharing sensitive health data, individuals often find themselves vulnerable. The interplay between innovation and privacy is complex and raises critical questions. Who truly safeguards our private details? What happens when sensitive information falls into the wrong hands?
Many individuals are unaware of how their personal records are accessed and utilized. Every time a person seeks medical help or engages with a health platform, data is generated. This data can encompass everything from treatment history to even genetic information. Such details are invaluable to various organizations. However, they can also lead to misuse, resulting in significant ramifications for patients.
Privacy violations can have profound consequences; they can result in identity theft and discrimination. Patients might hesitate to seek necessary treatments if they fear exposure. Additionally, trust in medical professionals and institutions could diminish sharply if individuals perceive a lack of safeguarding. Each breach, no matter how minor, chips away at the confidence that patients place in the entire system.
Legislation has evolved to address these growing concerns, but gaps remain. While laws aim to protect sensitive health details, enforcement can be inconsistent. Some organizations prioritize profit over patient confidentiality, leading to potential exploitation of personal records. Furthermore, many individuals may not fully understand their rights regarding their own health information. They might unwittingly consent to sharing their personal data under convoluted terms and conditions.
Transparency is paramount, yet often lacking in this landscape. Many people are not informed about how their information is being used or shared. Initiatives promoting clearer communication about data handling practices are essential. Awareness can empower patients, enabling them to ask pertinent questions and take control of their own privacy.
Ultimately, the balance between innovation in medical technology and respecting personal privacy remains precarious. As advances continue to flourish, so must the protocols designed to protect individuals. More robust measures are needed to ensure that sensitive health data is treated with the utmost respect and confidentiality. Only through a concerted effort can we hope to address these pressing issues effectively.
In summary, the protection of personal health records must be a priority for all stakeholders involved. With rising concerns about potential misuse, it’s crucial to foster an environment of trust and respect. By advocating for stringent policies and greater transparency, we can create a future where individuals feel secure in sharing their health information without fear of repercussion.
Impact on Patient Care and Outcomes
In recent years, the intersection of personal health records and analytics has garnered significant attention. The integration of information derived from various sources can enhance treatment efficiencies. However, this evolution brings with it a range of consequences for patient experiences and overall health results. While some may argue that sharing health data can streamline processes, others emphasize potential drawbacks.
When health information is utilized to inform clinical decisions, it can lead to improved outcomes. Efficient patient management can arise from the insights gleaned from collective health records. Early detection of diseases often hinges on access to comprehensive patient histories. Moreover, by analyzing trends across larger populations, practitioners can tailor interventions more effectively.
Nevertheless, such practices can inadvertently undermine the trust patients place in their providers. Confidentiality concerns continually loom large, casting a shadow over the benefits of shared information. Patients may feel uncertain about how their personal details are handled. They want to know: Who has access to this information? How is it being used?
Moreover, disparities in access to shared records can create inequalities. Patients from different backgrounds may experience varied benefits or detriments based on how their information is utilized. This discrepancy can result in a widening gap in health outcomes. Ultimately, the focus should remain on the patient, ensuring that all practices enhance their wellbeing.
To summarize, while the use of shared health insights has the potential to elevate patient care, the ethical considerations cannot be overlooked. Balancing the advantages of shared knowledge with the need for privacy is crucial. As we navigate this evolving landscape, it is imperative that we prioritize patient trust and equity in healthcare delivery. This delicate balance will shape future practices and standards in the industry.
Impact on Patient Care and Outcomes
In today’s interconnected world, the exchange of health-related information has transformed how medical services are delivered. This evolution holds the potential to enhance patient experiences while also posing new challenges. Imagine a scenario where healthcare providers have immediate access to a wealth of patient data, leading to more informed decisions. It could change the way diagnoses are made. Personalized treatment plans may become a standard rather than an exception.
However, the implications for patient care extend beyond immediate benefits. Enhanced access to comprehensive records can streamline workflows, reducing administrative burdens. This, in turn, allows medical professionals to dedicate more time to interacting with patients. When healthcare practitioners understand an individual’s complete medical history, they are better equipped to address unique needs. Communication improves, trust is built, and satisfaction levels rise. Yet, it is crucial to consider the ethical dimensions involved.
On the flip side, the potential for misuse exists, which could jeopardize patient trust. Individuals may feel hesitant to share critical information, fearing breaches of their confidentiality. This anxiety can inadvertently compromise the quality of care received. If healthcare insights are used inappropriately or without consent, the very fabric of doctor-patient relationships might fray. Thus, what seems advantageous on the surface could lead to significant setbacks if not managed responsibly.
As we navigate this complex landscape, it is essential to seek a balance. Ensuring robust security measures are in place can help mitigate concerns, fostering a culture of transparency. The ultimate goal should be to leverage shared insights for the betterment of patient outcomes. Enhanced collaboration among medical professionals can lead to innovation in treatment methodologies. Consequently, the future holds promise, but it also demands vigilance to protect what matters most: the well-being of patients.
In conclusion, the influence of shared health information on patient care is profound. As technology evolves, so too must our approaches to ethical considerations and patient engagement. The path forward requires continuous dialogue among stakeholders in the health sector. It’s not simply about exchanging remove information from Radaris; it’s about ensuring that every individual feels valued and understood in their journey toward health. Ultimately, the focus must remain on improving the patient experience while safeguarding their rights and trust.
Future Trends in Health Data Exchange

As the landscape of health information sharing evolves, several significant trends are emerging. These changes promise to reshape how medical knowledge is exchanged, stored, and applied in clinical settings. The increasing sophistication of technology fuels this transformation. Innovations are not just enhancing efficiency; they also aim to improve patient outcomes.
One major trend is the rise of interoperability. Systems are becoming more integrated, allowing different platforms to communicate seamlessly. Organizations are seeking to break down silos that have historically hindered collaboration. This connectivity fosters a more robust ecosystem for sharing insights and treatment options. When various systems work together, healthcare professionals can access comprehensive patient histories. This leads to more informed decision-making.
Another significant shift is the growing emphasis on patient empowerment. As individuals gain access to their own health records, they are becoming more involved in their treatment journeys. This trend is reshaping the traditional patient-provider dynamic. Patients now expect transparency and engagement in their care processes. With tools that allow them to track their health metrics, patients are taking charge like never before.
Artificial intelligence is also playing a crucial role in the evolution of health exchanges. Algorithms are increasingly used for predictive analytics, helping to identify potential health issues before they manifest. This technology enhances preventative care strategies, ultimately leading to better health outcomes. However, it also raises important ethical questions about the use of personal health information.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Interoperability | Systems are becoming integrated for seamless communication. |
| Patient Empowerment | Individuals gain access to their health records. |
| Artificial Intelligence | Predictive analytics enhance preventative care. |
| Blockchain Technology | Secure transactions and data integrity are prioritized. |
Furthermore, blockchain technology is emerging as a pivotal solution for ensuring data integrity. It provides a decentralized method for managing health information exchanges. This not only enhances security but also instills greater confidence among stakeholders. As trust becomes a cornerstone of health information sharing, blockchain’s role will only continue to expand.
In conclusion, the future presents exciting opportunities and challenges in health information exchange. The evolving landscape promises improved patient outcomes and enhanced operational efficiency. However, vigilance is essential to address the ethical and privacy concerns that accompany these innovations. As technology advances, it will be critical to strike a balance between accessibility and security, ensuring that the benefits are realized without compromising the well-being of individuals.
